OpenAPI 回呼¶
你可以建立一個含有「路徑操作(path operation)」的 API,該操作會觸發對某個「外部 API(external API)」的請求(通常由使用你 API 的同一位開發者提供)。
當你的 API 應用呼叫「外部 API」時發生的過程稱為「回呼(callback)」。因為外部開發者撰寫的軟體會先向你的 API 發出請求,接著你的 API 再「回呼」,也就是向(可能同一位開發者建立的)外部 API 發送請求。
在這種情況下,你可能想要文件化說明該外部 API 應該長什麼樣子。它應該有哪些「路徑操作」、應該接受什麼 body、應該回傳什麼 response,等等。
帶有回呼的應用¶
我們用一個例子來看。
想像你開發了一個允許建立發票的應用。
這些發票會有 id、title(可選)、customer 和 total。
你的 API 的使用者(外部開發者)會透過一個 POST 請求在你的 API 中建立一張發票。
然後你的 API 會(讓我們想像):
- 將發票寄給該外部開發者的某位客戶。
- 代收款項。
- 再把通知回傳給 API 使用者(外部開發者)。
- 這會透過從「你的 API」向該外部開發者提供的「外部 API」送出 POST 請求完成(這就是「回呼」)。
一般的 FastAPI 應用¶
先看看在加入回呼之前,一個一般的 API 應用會長什麼樣子。
它會有一個接收 Invoice body 的「路徑操作」,以及一個查詢參數 callback_url,其中包含用於回呼的 URL。
這部分很正常,多數程式碼你應該已經很熟悉了:
from fastapi import APIRouter, FastAPI
from pydantic import BaseModel, HttpUrl
app = FastAPI()
class Invoice(BaseModel):
id: str
title: str | None = None
customer: str
total: float
class InvoiceEvent(BaseModel):
description: str
paid: bool
class InvoiceEventReceived(BaseModel):
ok: bool
invoices_callback_router = APIRouter()
@invoices_callback_router.post(
"{$callback_url}/invoices/{$request.body.id}", response_model=InvoiceEventReceived
)
def invoice_notification(body: InvoiceEvent):
pass
@app.post("/invoices/", callbacks=invoices_callback_router.routes)
def create_invoice(invoice: Invoice, callback_url: HttpUrl | None = None):
"""
Create an invoice.
This will (let's imagine) let the API user (some external developer) create an
invoice.
And this path operation will:
* Send the invoice to the client.
* Collect the money from the client.
* Send a notification back to the API user (the external developer), as a callback.
* At this point is that the API will somehow send a POST request to the
external API with the notification of the invoice event
(e.g. "payment successful").
"""
# Send the invoice, collect the money, send the notification (the callback)
return {"msg": "Invoice received"}
Tip
callback_url 查詢參數使用的是 Pydantic 的 Url 型別。
唯一新的地方是在「路徑操作裝飾器」中加入參數 callbacks=invoices_callback_router.routes。我們接下來會看到那是什麼。
文件化回呼¶
實際的回呼程式碼會高度依賴你的 API 應用本身。
而且很可能每個應用都差很多。
它可能就只有一兩行,例如:
callback_url = "https://example.com/api/v1/invoices/events/"
httpx.post(callback_url, json={"description": "Invoice paid", "paid": True})
但回呼中最重要的部分,可能是在確保你的 API 使用者(外部開發者)能正確實作「外部 API」,符合「你的 API」在回呼請求 body 中要送出的資料格式,等等。
因此,接下來我們要加上用來「文件化」說明,該「外部 API」應該長什麼樣子,才能接收來自「你的 API」的回呼。
這份文件會出現在你的 API 的 Swagger UI /docs,讓外部開發者知道該如何建置「外部 API」。
這個範例不會實作回呼本身(那可能就只是一行程式碼),只會實作文件的部分。
撰寫回呼的文件化程式碼¶
這段程式碼在你的應用中不會被執行,我們只需要它來「文件化」說明那個「外部 API」應該長什麼樣子。
不過,你已經知道如何用 FastAPI 輕鬆為 API 建立自動文件。
所以我們會用同樣的方式,來文件化「外部 API」應該長什麼樣子... 也就是建立外部 API 應該實作的「路徑操作(們)」(那些「你的 API」會去呼叫的操作)。
Tip
在撰寫回呼的文件化程式碼時,把自己想像成那位「外部開發者」會很有幫助。而且你現在是在實作「外部 API」,不是「你的 API」。
暫時採用這個(外部開發者)的視角,有助於讓你更直覺地決定該把參數、body 的 Pydantic 模型、response 的模型等放在哪裡,對於那個「外部 API」會更清楚。
建立一個回呼用的 APIRouter¶
先建立一個新的 APIRouter,用來放一個或多個回呼。
from fastapi import APIRouter, FastAPI
from pydantic import BaseModel, HttpUrl
app = FastAPI()
class Invoice(BaseModel):
id: str
title: str | None = None
customer: str
total: float
class InvoiceEvent(BaseModel):
description: str
paid: bool
class InvoiceEventReceived(BaseModel):
ok: bool
invoices_callback_router = APIRouter()
@invoices_callback_router.post(
"{$callback_url}/invoices/{$request.body.id}", response_model=InvoiceEventReceived
)
def invoice_notification(body: InvoiceEvent):
pass
@app.post("/invoices/", callbacks=invoices_callback_router.routes)
def create_invoice(invoice: Invoice, callback_url: HttpUrl | None = None):
"""
Create an invoice.
This will (let's imagine) let the API user (some external developer) create an
invoice.
And this path operation will:
* Send the invoice to the client.
* Collect the money from the client.
* Send a notification back to the API user (the external developer), as a callback.
* At this point is that the API will somehow send a POST request to the
external API with the notification of the invoice event
(e.g. "payment successful").
"""
# Send the invoice, collect the money, send the notification (the callback)
return {"msg": "Invoice received"}
建立回呼的「路徑操作」¶
要建立回呼的「路徑操作」,就使用你上面建立的同一個 APIRouter。
它看起來就像一般的 FastAPI「路徑操作」:
- 可能需要宣告它應該接收的 body,例如
body: InvoiceEvent。 - 也可以宣告它應該回傳的 response,例如
response_model=InvoiceEventReceived。
from fastapi import APIRouter, FastAPI
from pydantic import BaseModel, HttpUrl
app = FastAPI()
class Invoice(BaseModel):
id: str
title: str | None = None
customer: str
total: float
class InvoiceEvent(BaseModel):
description: str
paid: bool
class InvoiceEventReceived(BaseModel):
ok: bool
invoices_callback_router = APIRouter()
@invoices_callback_router.post(
"{$callback_url}/invoices/{$request.body.id}", response_model=InvoiceEventReceived
)
def invoice_notification(body: InvoiceEvent):
pass
@app.post("/invoices/", callbacks=invoices_callback_router.routes)
def create_invoice(invoice: Invoice, callback_url: HttpUrl | None = None):
"""
Create an invoice.
This will (let's imagine) let the API user (some external developer) create an
invoice.
And this path operation will:
* Send the invoice to the client.
* Collect the money from the client.
* Send a notification back to the API user (the external developer), as a callback.
* At this point is that the API will somehow send a POST request to the
external API with the notification of the invoice event
(e.g. "payment successful").
"""
# Send the invoice, collect the money, send the notification (the callback)
return {"msg": "Invoice received"}
和一般「路徑操作」相比有兩個主要差異:
- 不需要任何實際程式碼,因為你的應用永遠不會呼叫這段程式。它只用來文件化「外部 API」。因此函式可以只有
pass。 - 「路徑」可以包含一個 OpenAPI 3 表達式(見下文),可使用參數與原始送到「你的 API」的請求中的部分欄位。
回呼路徑表達式¶
回呼的「路徑」可以包含一個 OpenAPI 3 表達式,能引用原本送到「你的 API」的請求中的部分內容。
在這個例子中,它是一個 str:
"{$callback_url}/invoices/{$request.body.id}"
所以,如果你的 API 使用者(外部開發者)向「你的 API」送出這樣的請求:
https://yourapi.com/invoices/?callback_url=https://www.external.org/events
並附上這個 JSON body:
{
"id": "2expen51ve",
"customer": "Mr. Richie Rich",
"total": "9999"
}
那麼「你的 API」會處理這張發票,並在稍後某個時點,向 callback_url(也就是「外部 API」)送出回呼請求:
https://www.external.org/events/invoices/2expen51ve
其 JSON body 大致包含:
{
"description": "Payment celebration",
"paid": true
}
而它會預期該「外部 API」回傳的 JSON body 例如:
{
"ok": true
}
Tip
注意回呼所用的 URL,包含了在查詢參數 callback_url 中收到的 URL(https://www.external.org/events),以及來自 JSON body 內的發票 id(2expen51ve)。
加入回呼 router¶
此時你已經在先前建立的回呼 router 中,擁有所需的回呼「路徑操作(們)」(也就是「外部開發者」應該在「外部 API」中實作的那些)。
現在在「你的 API 的路徑操作裝飾器」中使用參數 callbacks,將該回呼 router 的屬性 .routes(實際上就是一個由路由/「路徑操作」所組成的 list)傳入:
from fastapi import APIRouter, FastAPI
from pydantic import BaseModel, HttpUrl
app = FastAPI()
class Invoice(BaseModel):
id: str
title: str | None = None
customer: str
total: float
class InvoiceEvent(BaseModel):
description: str
paid: bool
class InvoiceEventReceived(BaseModel):
ok: bool
invoices_callback_router = APIRouter()
@invoices_callback_router.post(
"{$callback_url}/invoices/{$request.body.id}", response_model=InvoiceEventReceived
)
def invoice_notification(body: InvoiceEvent):
pass
@app.post("/invoices/", callbacks=invoices_callback_router.routes)
def create_invoice(invoice: Invoice, callback_url: HttpUrl | None = None):
"""
Create an invoice.
This will (let's imagine) let the API user (some external developer) create an
invoice.
And this path operation will:
* Send the invoice to the client.
* Collect the money from the client.
* Send a notification back to the API user (the external developer), as a callback.
* At this point is that the API will somehow send a POST request to the
external API with the notification of the invoice event
(e.g. "payment successful").
"""
# Send the invoice, collect the money, send the notification (the callback)
return {"msg": "Invoice received"}
Tip
注意你傳給 callback= 的不是整個 router 本身(invoices_callback_router),而是它的屬性 .routes,也就是 invoices_callback_router.routes。
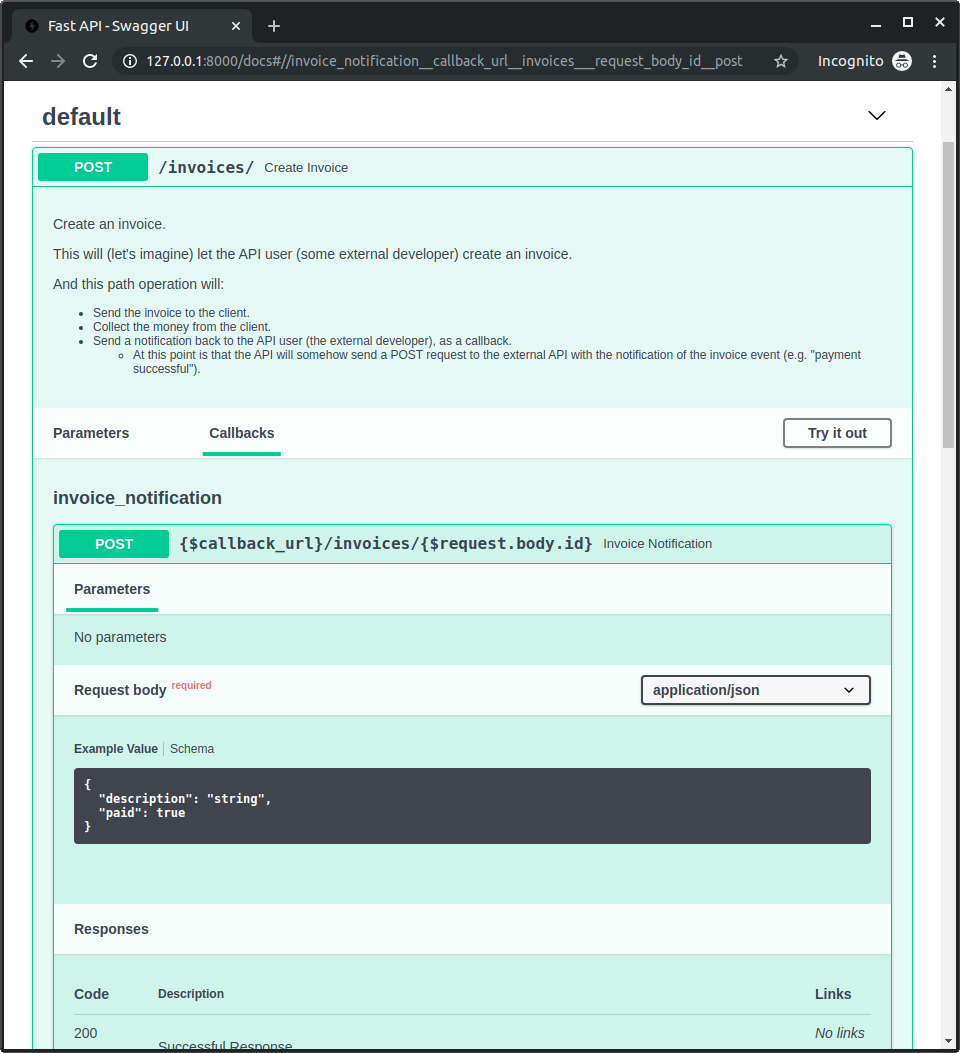
檢查文件¶
現在你可以啟動應用,並前往 http://127.0.0.1:8000/docs。
你會在文件中看到你的「路徑操作」包含一個「Callbacks」區塊,顯示「外部 API」應該長什麼樣子: