OpenAPI コールバック¶
🌐 AI と人間による翻訳
この翻訳は、人間のガイドに基づいて AI によって作成されました。🤝
原文の意図を取り違えていたり、不自然な表現になっている可能性があります。🤖
AI LLM をより適切に誘導するのを手伝う ことで、この翻訳を改善できます。
あなたは、path operation を持つ API を作成し、他者(多くの場合、あなたの API を「利用する」同一の開発者)が作成した 外部 API へリクエストをトリガーできるようにできます。
あなたの API アプリが 外部 API を呼び出すときに起きる処理は「コールバック」と呼ばれます。なぜなら、外部開発者が作成したソフトウェアがあなたの API にリクエストを送り、その後であなたの API が「呼び返し」、外部 API(おそらく同じ開発者が作成)へリクエストを送るためです。
この場合、その 外部 API がどのようである「べき」かをドキュメント化したくなるでしょう。どんな path operation を持ち、どんなボディを受け取り、どんなレスポンスを返すか、などです。
コールバックのあるアプリ¶
例で見ていきます。
あなたが請求書を作成できるアプリを開発していると想像してください。
これらの請求書は id、title(任意)、customer、total を持ちます。
あなたの API の利用者(外部開発者)は、POST リクエストであなたの API に請求書を作成します。
その後、あなたの API は(仮にこうしましょう):
- 外部開発者の顧客に請求書を送ります。
- 代金を回収します。
- API 利用者(外部開発者)に通知を送り返します。
- これは(あなたの API から)外部開発者が提供する 外部 API に POST リクエストを送ることで行われます(これが「コールバック」です)。
通常の FastAPI アプリ¶
まず、コールバックを追加する前の通常の API アプリがどうなるか見てみましょう。
Invoice ボディを受け取り、クエリパラメータ callback_url にコールバック用の URL を含める path operation を持ちます。
この部分はとても普通で、ほとんどのコードはすでに見覚えがあるはずです:
from fastapi import APIRouter, FastAPI
from pydantic import BaseModel, HttpUrl
app = FastAPI()
class Invoice(BaseModel):
id: str
title: str | None = None
customer: str
total: float
class InvoiceEvent(BaseModel):
description: str
paid: bool
class InvoiceEventReceived(BaseModel):
ok: bool
invoices_callback_router = APIRouter()
@invoices_callback_router.post(
"{$callback_url}/invoices/{$request.body.id}", response_model=InvoiceEventReceived
)
def invoice_notification(body: InvoiceEvent):
pass
@app.post("/invoices/", callbacks=invoices_callback_router.routes)
def create_invoice(invoice: Invoice, callback_url: HttpUrl | None = None):
"""
Create an invoice.
This will (let's imagine) let the API user (some external developer) create an
invoice.
And this path operation will:
* Send the invoice to the client.
* Collect the money from the client.
* Send a notification back to the API user (the external developer), as a callback.
* At this point is that the API will somehow send a POST request to the
external API with the notification of the invoice event
(e.g. "payment successful").
"""
# Send the invoice, collect the money, send the notification (the callback)
return {"msg": "Invoice received"}
豆知識
callback_url クエリパラメータは、Pydantic の Url 型を使用します。
唯一の新しい点は、path operation デコレータの引数として callbacks=invoices_callback_router.routes を渡すことです。これが何かは次で見ます。
コールバックのドキュメント化¶
実際のコールバックのコードは、あなた自身の API アプリに大きく依存します。
そしてアプリごとに大きく異なるでしょう。
それは次のように 1、2 行のコードかもしれません:
callback_url = "https://example.com/api/v1/invoices/events/"
httpx.post(callback_url, json={"description": "Invoice paid", "paid": True})
しかし、おそらくコールバックで最も重要な点は、あなたの API 利用者(外部開発者)が、あなたの API がコールバックのリクエストボディなどで送るデータに従って、外部 API を正しく実装することを確実にすることです。
そこで次に行うのは、あなたの API からのコールバックを受け取るために、その 外部 API がどうあるべきかをドキュメント化するコードを追加することです。
そのドキュメントはあなたの API の /docs の Swagger UI に表示され、外部開発者に 外部 API の作り方を知らせます。
この例ではコールバック自体は実装しません(それは 1 行のコードでもよいでしょう)。ドキュメント部分のみです。
コールバックのドキュメント用コードを書く¶
このコードはあなたのアプリで実行されません。外部 API がどうあるべきかをドキュメント化するためだけに必要です。
しかし、あなたはすでに FastAPI で API の自動ドキュメントを簡単に作る方法を知っています。
その知識を使って、外部 API がどうあるべきかをドキュメント化します……つまり、外部 API が実装すべき path operation(s)(あなたの API が呼び出すもの)を作成します。
豆知識
コールバックをドキュメント化するコードを書くときは、あなたがその「外部開発者」だと想像するのが役に立つかもしれません。いま実装しているのは「あなたの API」ではなく、外部 API です。
この(外部開発者の)視点を一時的に採用すると、その 外部 API に対してパラメータ、ボディ用の Pydantic モデル、レスポンスなどをどこに置くのが自然かがより明確に感じられるでしょう。
コールバック用 APIRouter を作成¶
まず、1 つ以上のコールバックを含む新しい APIRouter を作成します。
from fastapi import APIRouter, FastAPI
from pydantic import BaseModel, HttpUrl
app = FastAPI()
class Invoice(BaseModel):
id: str
title: str | None = None
customer: str
total: float
class InvoiceEvent(BaseModel):
description: str
paid: bool
class InvoiceEventReceived(BaseModel):
ok: bool
invoices_callback_router = APIRouter()
@invoices_callback_router.post(
"{$callback_url}/invoices/{$request.body.id}", response_model=InvoiceEventReceived
)
def invoice_notification(body: InvoiceEvent):
pass
@app.post("/invoices/", callbacks=invoices_callback_router.routes)
def create_invoice(invoice: Invoice, callback_url: HttpUrl | None = None):
"""
Create an invoice.
This will (let's imagine) let the API user (some external developer) create an
invoice.
And this path operation will:
* Send the invoice to the client.
* Collect the money from the client.
* Send a notification back to the API user (the external developer), as a callback.
* At this point is that the API will somehow send a POST request to the
external API with the notification of the invoice event
(e.g. "payment successful").
"""
# Send the invoice, collect the money, send the notification (the callback)
return {"msg": "Invoice received"}
コールバックの path operation を作成¶
上で作成したのと同じ APIRouter を使って、コールバックの path operation を作成します。
見た目は通常の FastAPI の path operation と同じです:
- 受け取るボディの宣言(例:
body: InvoiceEvent)が必要でしょう。 - 返すレスポンスの宣言(例:
response_model=InvoiceEventReceived)も持てます。
from fastapi import APIRouter, FastAPI
from pydantic import BaseModel, HttpUrl
app = FastAPI()
class Invoice(BaseModel):
id: str
title: str | None = None
customer: str
total: float
class InvoiceEvent(BaseModel):
description: str
paid: bool
class InvoiceEventReceived(BaseModel):
ok: bool
invoices_callback_router = APIRouter()
@invoices_callback_router.post(
"{$callback_url}/invoices/{$request.body.id}", response_model=InvoiceEventReceived
)
def invoice_notification(body: InvoiceEvent):
pass
@app.post("/invoices/", callbacks=invoices_callback_router.routes)
def create_invoice(invoice: Invoice, callback_url: HttpUrl | None = None):
"""
Create an invoice.
This will (let's imagine) let the API user (some external developer) create an
invoice.
And this path operation will:
* Send the invoice to the client.
* Collect the money from the client.
* Send a notification back to the API user (the external developer), as a callback.
* At this point is that the API will somehow send a POST request to the
external API with the notification of the invoice event
(e.g. "payment successful").
"""
# Send the invoice, collect the money, send the notification (the callback)
return {"msg": "Invoice received"}
通常の path operation と異なる主な点が 2 つあります:
- 実際のコードは不要です。あなたのアプリはこのコードを決して呼びません。これは 外部 API をドキュメント化するためだけに使われます。したがって、関数本体は
passで構いません。 - パス には、あなたの API に送られた元のリクエストのパラメータや一部を変数として使える OpenAPI 3 の式(後述)を含められます。
コールバックのパス式¶
コールバックの パス には、あなたの API に送られた元のリクエストの一部を含められる OpenAPI 3 の式を使用できます。
この例では、str は次のとおりです:
"{$callback_url}/invoices/{$request.body.id}"
つまり、あなたの API 利用者(外部開発者)が あなたの API に次のようにリクエストを送った場合:
https://yourapi.com/invoices/?callback_url=https://www.external.org/events
JSON ボディは:
{
"id": "2expen51ve",
"customer": "Mr. Richie Rich",
"total": "9999"
}
その後 あなたの API は請求書を処理し、のちほど callback_url(外部 API)へコールバックのリクエストを送ります:
https://www.external.org/events/invoices/2expen51ve
JSON ボディは次のような内容です:
{
"description": "Payment celebration",
"paid": true
}
そして 外部 API からは次のような JSON ボディのレスポンスを期待します:
{
"ok": true
}
豆知識
使用されるコールバック URL には、クエリパラメータ callback_url(https://www.external.org/events)で受け取った URL と、JSON ボディ内の請求書 id(2expen51ve)が含まれている点に注目してください。
コールバック用ルーターを追加¶
これで、上で作成したコールバック用ルーター内に、必要なコールバックの path operation(s)(外部開発者 が 外部 API に実装すべきもの)が用意できました。
次に、あなたの API の path operation デコレータの callbacks パラメータに、そのコールバック用ルーターの属性 .routes(実体はルート/path operations の list)を渡します:
from fastapi import APIRouter, FastAPI
from pydantic import BaseModel, HttpUrl
app = FastAPI()
class Invoice(BaseModel):
id: str
title: str | None = None
customer: str
total: float
class InvoiceEvent(BaseModel):
description: str
paid: bool
class InvoiceEventReceived(BaseModel):
ok: bool
invoices_callback_router = APIRouter()
@invoices_callback_router.post(
"{$callback_url}/invoices/{$request.body.id}", response_model=InvoiceEventReceived
)
def invoice_notification(body: InvoiceEvent):
pass
@app.post("/invoices/", callbacks=invoices_callback_router.routes)
def create_invoice(invoice: Invoice, callback_url: HttpUrl | None = None):
"""
Create an invoice.
This will (let's imagine) let the API user (some external developer) create an
invoice.
And this path operation will:
* Send the invoice to the client.
* Collect the money from the client.
* Send a notification back to the API user (the external developer), as a callback.
* At this point is that the API will somehow send a POST request to the
external API with the notification of the invoice event
(e.g. "payment successful").
"""
# Send the invoice, collect the money, send the notification (the callback)
return {"msg": "Invoice received"}
豆知識
callback= に渡すのはルーター本体(invoices_callback_router)ではなく、属性 .routes(invoices_callback_router.routes)である点に注意してください。
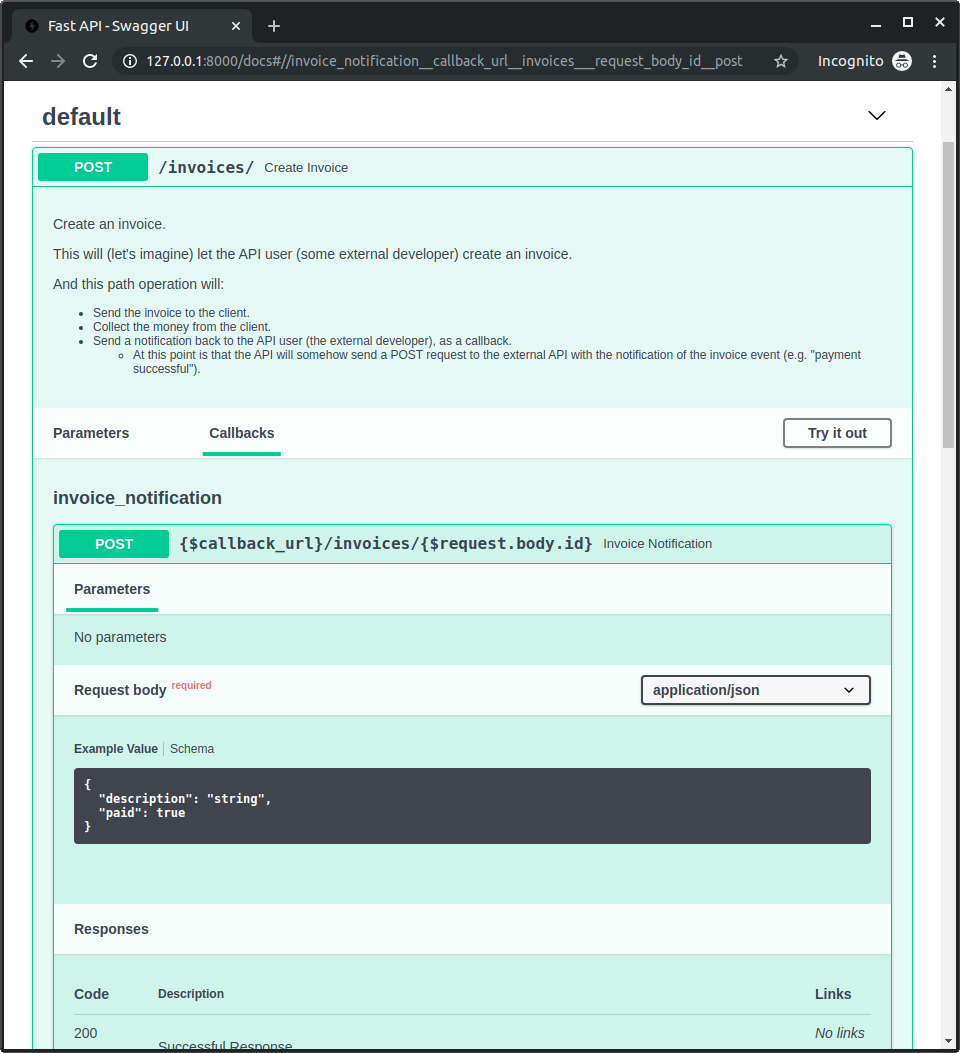
ドキュメントを確認¶
アプリを起動して http://127.0.0.1:8000/docs にアクセスします。
あなたの path operation に「Callbacks」セクションが含まれ、外部 API がどうあるべきかが表示されているのが確認できます: