路径操作配置¶
路径操作装饰器支持多种配置参数。
警告
注意:以下参数应直接传递给路径操作装饰器,不能传递给路径操作函数。
响应状态码¶
可以在路径操作的响应中定义(HTTP)status_code。
可以直接传递 int 代码,比如 404。
如果记不住数字码的含义,也可以用 status 的快捷常量:
from fastapi import FastAPI, status
from pydantic import BaseModel
app = FastAPI()
class Item(BaseModel):
name: str
description: str | None = None
price: float
tax: float | None = None
tags: set[str] = set()
@app.post("/items/", status_code=status.HTTP_201_CREATED)
async def create_item(item: Item) -> Item:
return item
该状态码会用于响应中,并会被添加到 OpenAPI 概图。
技术细节
也可以使用 from starlette import status 导入状态码。
FastAPI 提供的 fastapi.status 与 starlette.status 相同,方便你作为开发者使用。实际上它直接来自 Starlette。
标签¶
可以通过传入由 str 组成的 list(通常只有一个 str)的参数 tags,为路径操作添加标签:
from fastapi import FastAPI
from pydantic import BaseModel
app = FastAPI()
class Item(BaseModel):
name: str
description: str | None = None
price: float
tax: float | None = None
tags: set[str] = set()
@app.post("/items/", tags=["items"])
async def create_item(item: Item) -> Item:
return item
@app.get("/items/", tags=["items"])
async def read_items():
return [{"name": "Foo", "price": 42}]
@app.get("/users/", tags=["users"])
async def read_users():
return [{"username": "johndoe"}]
OpenAPI 概图会自动添加标签,供 API 文档接口使用:
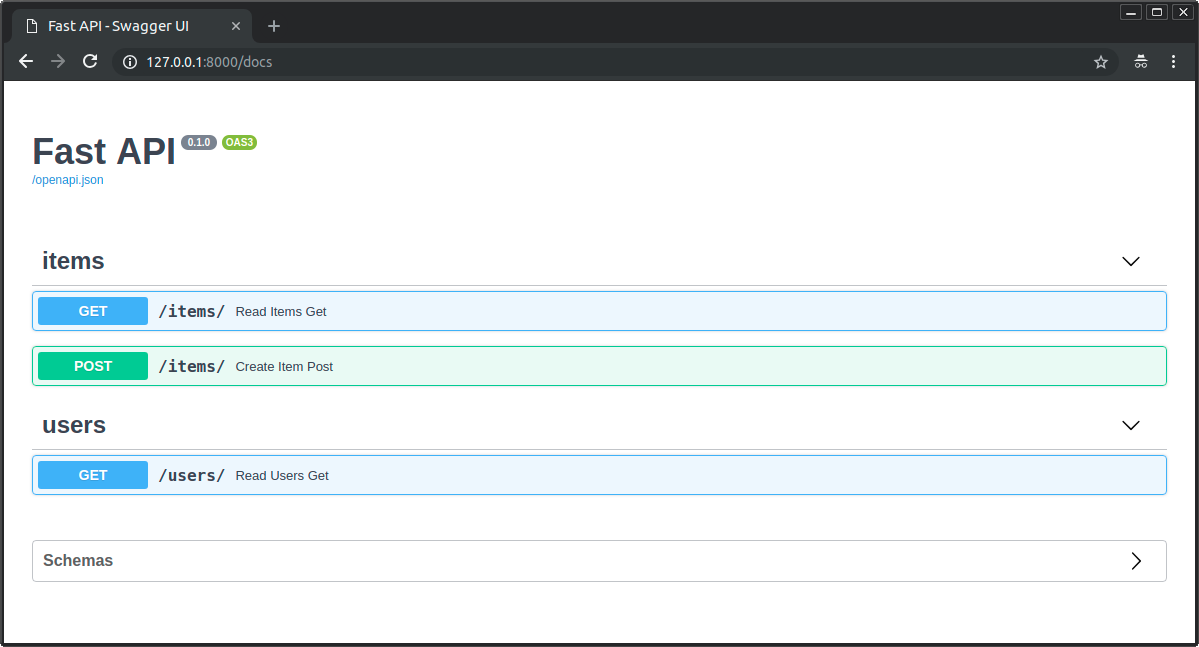
使用 Enum 的标签¶
如果你的应用很大,可能会积累出很多标签,你会希望确保相关的路径操作始终使用相同的标签。
这种情况下,把标签存放在 Enum 中会更合适。
FastAPI 对此的支持与使用普通字符串相同:
from enum import Enum
from fastapi import FastAPI
app = FastAPI()
class Tags(Enum):
items = "items"
users = "users"
@app.get("/items/", tags=[Tags.items])
async def get_items():
return ["Portal gun", "Plumbus"]
@app.get("/users/", tags=[Tags.users])
async def read_users():
return ["Rick", "Morty"]
摘要和描述¶
可以添加 summary 和 description:
from fastapi import FastAPI
from pydantic import BaseModel
app = FastAPI()
class Item(BaseModel):
name: str
description: str | None = None
price: float
tax: float | None = None
tags: set[str] = set()
@app.post(
"/items/",
summary="Create an item",
description="Create an item with all the information, name, description, price, tax and a set of unique tags",
)
async def create_item(item: Item) -> Item:
return item
从 docstring 获取描述¶
描述内容比较长且占用多行时,可以在函数的 docstring 中声明路径操作的描述,FastAPI 会从中读取。
文档字符串支持 Markdown,能正确解析和显示 Markdown 的内容,但要注意文档字符串的缩进。
from fastapi import FastAPI
from pydantic import BaseModel
app = FastAPI()
class Item(BaseModel):
name: str
description: str | None = None
price: float
tax: float | None = None
tags: set[str] = set()
@app.post("/items/", summary="Create an item")
async def create_item(item: Item) -> Item:
"""
Create an item with all the information:
- **name**: each item must have a name
- **description**: a long description
- **price**: required
- **tax**: if the item doesn't have tax, you can omit this
- **tags**: a set of unique tag strings for this item
"""
return item
它会在交互式文档中使用:
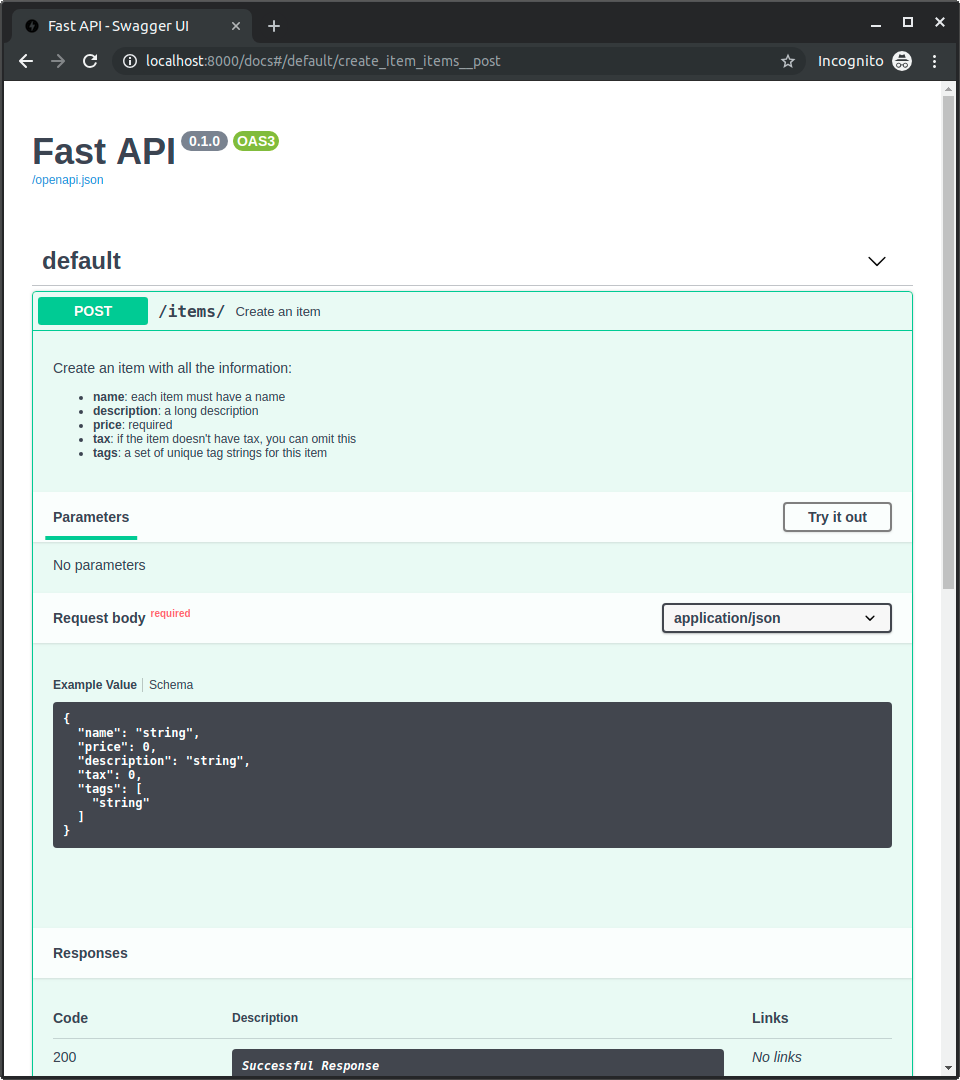
响应描述¶
response_description 参数用于定义响应的描述说明:
from fastapi import FastAPI
from pydantic import BaseModel
app = FastAPI()
class Item(BaseModel):
name: str
description: str | None = None
price: float
tax: float | None = None
tags: set[str] = set()
@app.post(
"/items/",
summary="Create an item",
response_description="The created item",
)
async def create_item(item: Item) -> Item:
"""
Create an item with all the information:
- **name**: each item must have a name
- **description**: a long description
- **price**: required
- **tax**: if the item doesn't have tax, you can omit this
- **tags**: a set of unique tag strings for this item
"""
return item
信息
注意,response_description 只用于描述响应,description 一般则用于描述路径操作。
检查
OpenAPI 规定每个路径操作都要有响应描述。
如果没有定义响应描述,FastAPI 则自动生成内容为 "Successful response" 的响应描述。
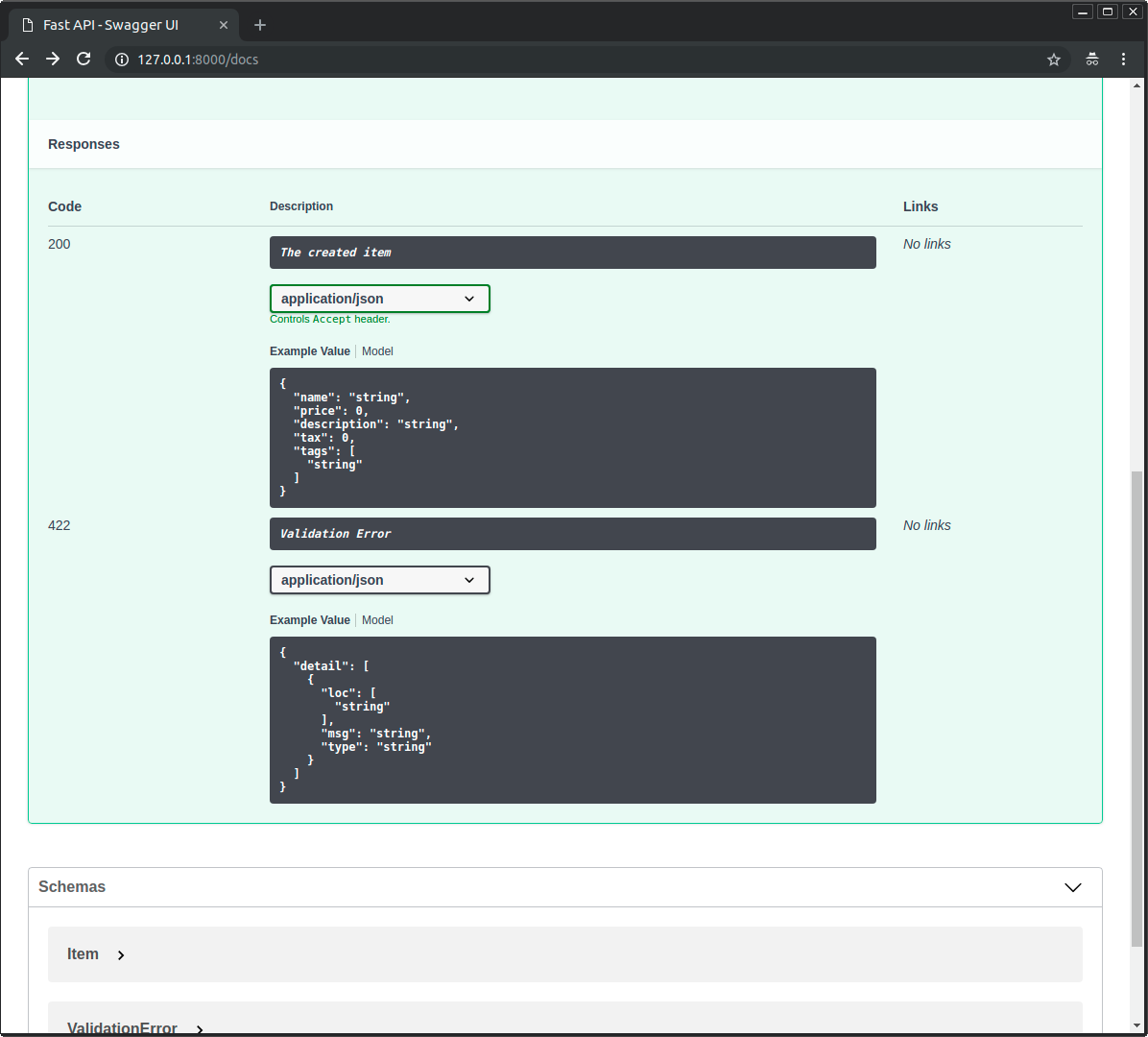
弃用路径操作¶
如果需要把路径操作标记为弃用,但不删除它,可以传入 deprecated 参数:
from fastapi import FastAPI
app = FastAPI()
@app.get("/items/", tags=["items"])
async def read_items():
return [{"name": "Foo", "price": 42}]
@app.get("/users/", tags=["users"])
async def read_users():
return [{"username": "johndoe"}]
@app.get("/elements/", tags=["items"], deprecated=True)
async def read_elements():
return [{"item_id": "Foo"}]
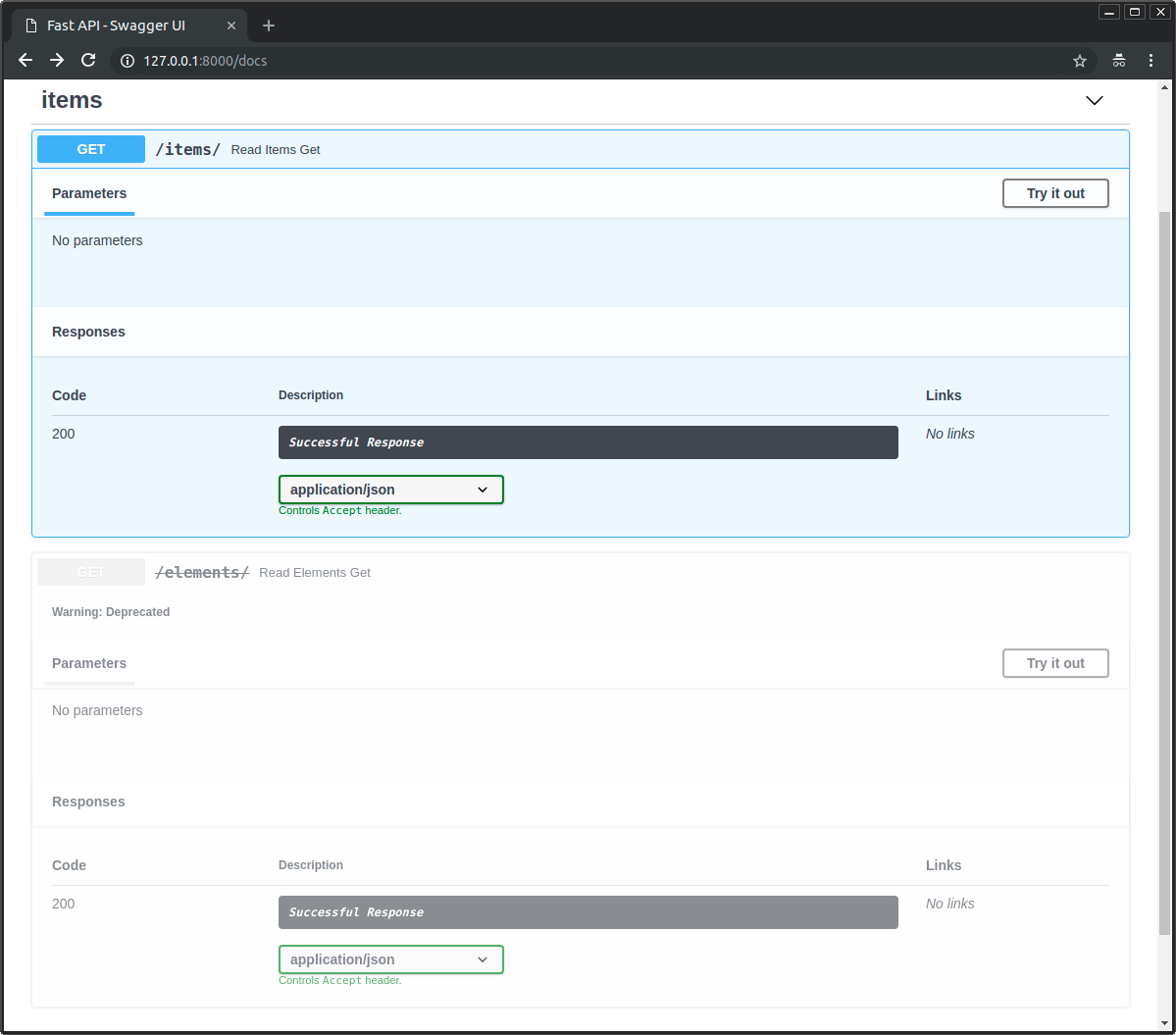
API 文档会把该路径操作标记为弃用:
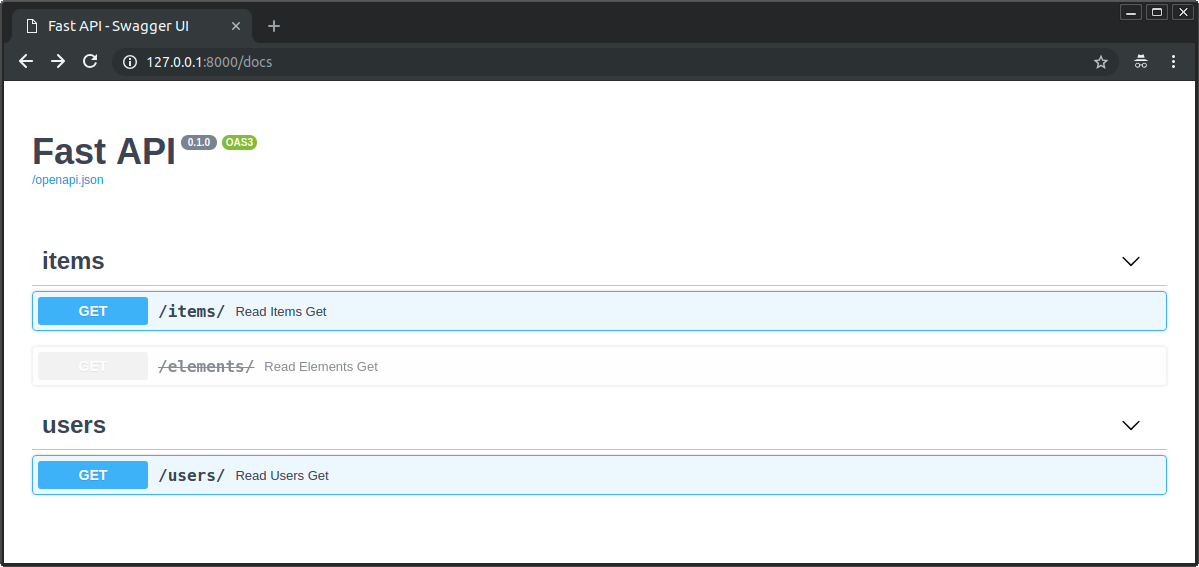
下图显示了正常路径操作与弃用路径操作 的区别:
小结¶
通过传递参数给路径操作装饰器,即可轻松地配置路径操作、添加元数据。