第一步¶
最簡單的 FastAPI 檔案可能看起來像這樣:
from fastapi import FastAPI
app = FastAPI()
@app.get("/")
async def root():
return {"message": "Hello World"}
將其複製到一個名為 main.py 的文件中。
執行即時重新載入伺服器(live server):
$ <font color="#4E9A06">fastapi</font> dev <u style="text-decoration-style:solid">main.py</u>
<span style="background-color:#009485"><font color="#D3D7CF"> FastAPI </font></span> Starting development server 🚀
Searching for package file structure from directories
with <font color="#3465A4">__init__.py</font> files
Importing from <font color="#75507B">/home/user/code/</font><font color="#AD7FA8">awesomeapp</font>
<span style="background-color:#007166"><font color="#D3D7CF"> module </font></span> 🐍 main.py
<span style="background-color:#007166"><font color="#D3D7CF"> code </font></span> Importing the FastAPI app object from the module with
the following code:
<u style="text-decoration-style:solid">from </u><u style="text-decoration-style:solid"><b>main</b></u><u style="text-decoration-style:solid"> import </u><u style="text-decoration-style:solid"><b>app</b></u>
<span style="background-color:#007166"><font color="#D3D7CF"> app </font></span> Using import string: <font color="#3465A4">main:app</font>
<span style="background-color:#007166"><font color="#D3D7CF"> server </font></span> Server started at <font color="#729FCF"><u style="text-decoration-style:solid">http://127.0.0.1:8000</u></font>
<span style="background-color:#007166"><font color="#D3D7CF"> server </font></span> Documentation at <font color="#729FCF"><u style="text-decoration-style:solid">http://127.0.0.1:8000/docs</u></font>
<span style="background-color:#007166"><font color="#D3D7CF"> tip </font></span> Running in development mode, for production use:
<b>fastapi run</b>
Logs:
<span style="background-color:#007166"><font color="#D3D7CF"> INFO </font></span> Will watch for changes in these directories:
<b>[</b><font color="#4E9A06">'/home/user/code/awesomeapp'</font><b>]</b>
<span style="background-color:#007166"><font color="#D3D7CF"> INFO </font></span> Uvicorn running on <font color="#729FCF"><u style="text-decoration-style:solid">http://127.0.0.1:8000</u></font> <b>(</b>Press CTRL+C
to quit<b>)</b>
<span style="background-color:#007166"><font color="#D3D7CF"> INFO </font></span> Started reloader process <b>[</b><font color="#34E2E2"><b>383138</b></font><b>]</b> using WatchFiles
<span style="background-color:#007166"><font color="#D3D7CF"> INFO </font></span> Started server process <b>[</b><font color="#34E2E2"><b>383153</b></font><b>]</b>
<span style="background-color:#007166"><font color="#D3D7CF"> INFO </font></span> Waiting for application startup.
<span style="background-color:#007166"><font color="#D3D7CF"> INFO </font></span> Application startup complete.
在輸出中,有一列類似於:
INFO: Uvicorn running on http://127.0.0.1:8000 (Press CTRL+C to quit)
那列顯示了你的應用程式正在本地端機器上運行的 URL。
查看它¶
在瀏覽器中打開 http://127.0.0.1:8000.
你將看到如下的 JSON 回應:
{"message": "Hello World"}
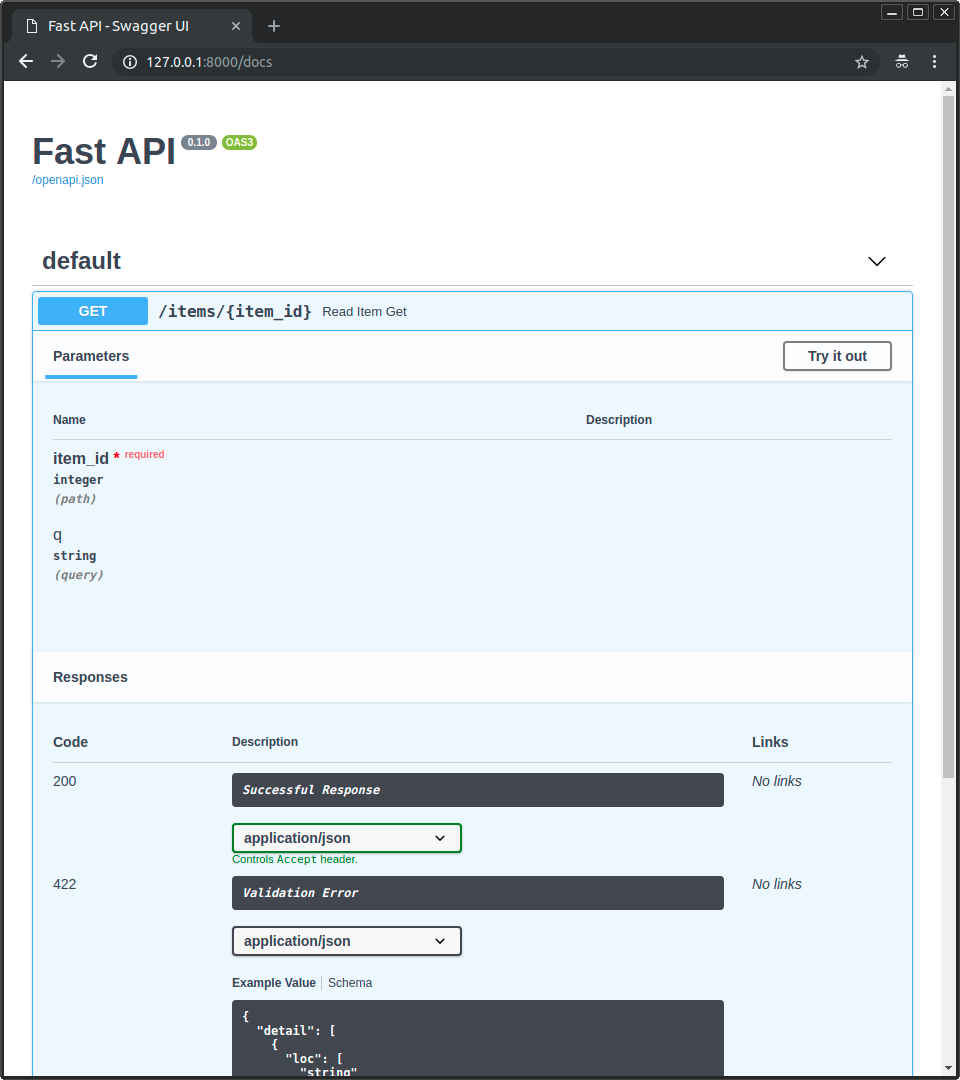
互動式 API 文件¶
現在,前往 http://127.0.0.1:8000/docs.
你將看到自動的互動式 API 文件(由 Swagger UI 提供):
替代 API 文件¶
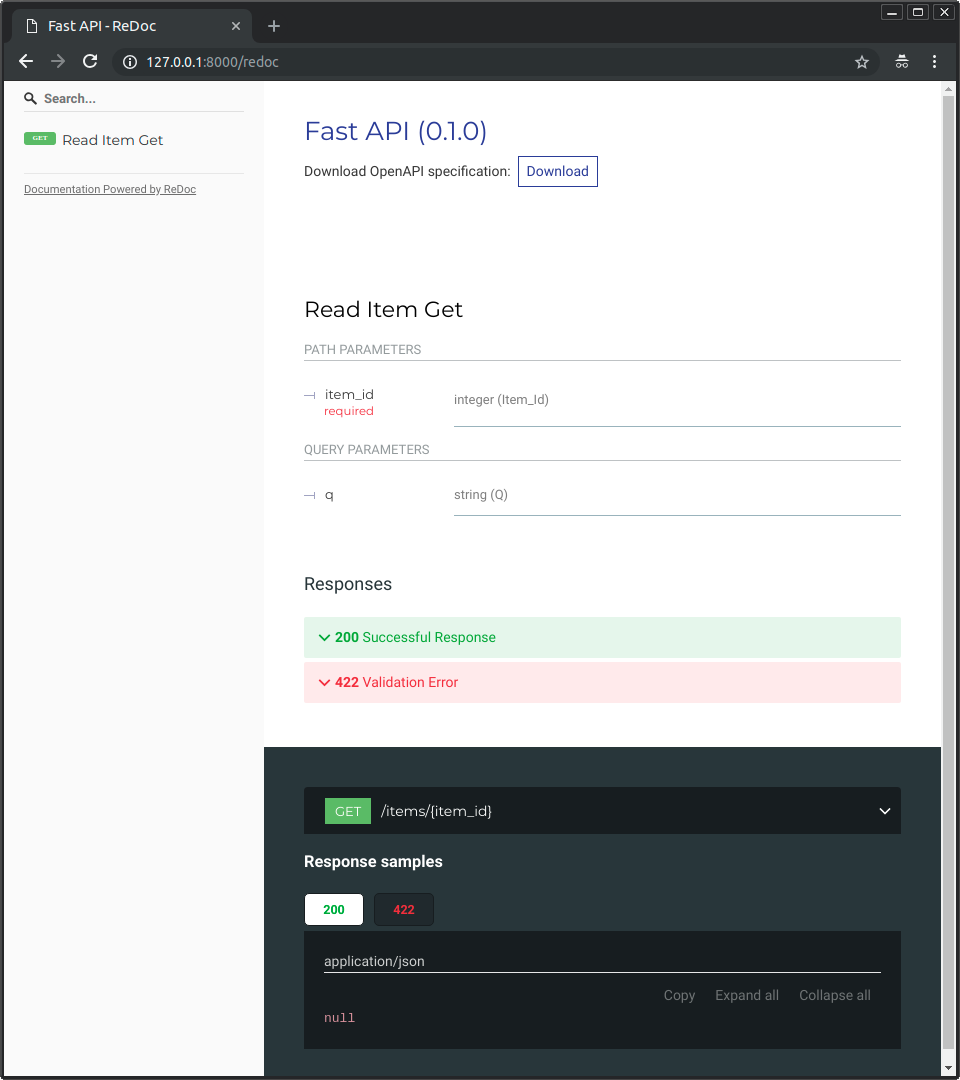
現在,前往 http://127.0.0.1:8000/redoc.
你將看到另一種自動文件(由 ReDoc 提供):
OpenAPI¶
FastAPI 使用定義 API 的 OpenAPI 標準來生成一個「schema」,涵蓋你的全部 API。
「Schema」¶
「schema」是對某個事物的定義或描述。它並不是實作它的程式碼,而僅僅是一個抽象的描述。
API 「schema」¶
在這種情況下,OpenAPI 是一個規範,它規定了如何定義 API 的 schema。
這個 schema 定義包含了你的 API 路徑、可能接收的參數等內容。
資料「schema」¶
「schema」這個術語也可能指某些資料的結構,比如 JSON 內容的結構。
在這種情況下,它指的是 JSON 的屬性、資料型別等。
OpenAPI 和 JSON Schema¶
OpenAPI 為你的 API 定義了 API 的 schema。而該 schema 會包含你的 API 所傳送與接收資料的定義(或稱「schemas」),使用 JSON Schema,這是 JSON 資料 schema 的標準。
檢查 openapi.json¶
如果你好奇原始的 OpenAPI schema 長什麼樣子,FastAPI 會自動生成一個包含所有 API 描述的 JSON(schema)。
你可以直接在 http://127.0.0.1:8000/openapi.json 查看它。
它會顯示一個 JSON,類似於:
{
"openapi": "3.1.0",
"info": {
"title": "FastAPI",
"version": "0.1.0"
},
"paths": {
"/items/": {
"get": {
"responses": {
"200": {
"description": "Successful Response",
"content": {
"application/json": {
...
OpenAPI 的用途¶
OpenAPI schema 驅動了兩個互動式文件系統。
而且有許多替代方案,所有這些都是基於 OpenAPI。你可以輕鬆地將任何這些替代方案添加到使用 FastAPI 建置的應用程式中。
你也可以用它自動生成程式碼,讓用戶端與你的 API 通訊。例如前端、手機或物聯網(IoT)應用程式。
部署你的應用程式(可選)¶
你可以選擇將你的 FastAPI 應用程式部署到 FastAPI Cloud,如果還沒有,去加入候補名單吧。🚀
如果你已經有 FastAPI Cloud 帳號(我們已從候補名單邀請你 😉),你可以用一個指令部署你的應用程式。
部署之前,先確保你已登入:
$ fastapi login
You are logged in to FastAPI Cloud 🚀
接著部署你的應用程式:
$ fastapi deploy
Deploying to FastAPI Cloud...
✅ Deployment successful!
🐔 Ready the chicken! Your app is ready at https://myapp.fastapicloud.dev
就這樣!現在你可以透過該 URL 存取你的應用程式了。✨
逐步回顧¶
第一步:引入 FastAPI¶
from fastapi import FastAPI
app = FastAPI()
@app.get("/")
async def root():
return {"message": "Hello World"}
FastAPI 是一個 Python 類別,提供所有 API 的全部功能。
第二步:建立一個 FastAPI「實例」¶
from fastapi import FastAPI
app = FastAPI()
@app.get("/")
async def root():
return {"message": "Hello World"}
這裡的 app 變數將會是 FastAPI 類別的「實例」。
這將是你建立所有 API 的主要互動點。
第三步:建立一個「路徑操作」¶
路徑¶
這裡的「路徑」指的是 URL 中自第一個 / 以後的部分。
例如,在 URL 中:
https://example.com/items/foo
……的路徑將會是:
/items/foo
Info
「路徑」也常被稱為「端點 endpoint」或「路由 route」。
在建置 API 時,「路徑」是分離「關注點」和「資源」的主要方式。
操作¶
這裡的「操作」指的是 HTTP 的「方法」之一。
其中包括:
POSTGETPUTDELETE
……以及更少見的:
OPTIONSHEADPATCHTRACE
在 HTTP 協定中,你可以使用這些「方法」之一(或更多)與每個路徑進行通信。
在建置 API 時,你通常使用這些特定的 HTTP 方法來執行特定的動作。
通常你使用:
POST:用來建立資料。GET:用來讀取資料。PUT:用來更新資料。DELETE:用來刪除資料。
所以,在 OpenAPI 中,每個 HTTP 方法都被稱為「操作」。
我們將會稱它們為「操作」。
定義一個「路徑操作裝飾器」¶
from fastapi import FastAPI
app = FastAPI()
@app.get("/")
async def root():
return {"message": "Hello World"}
@app.get("/") 告訴 FastAPI 那個函式負責處理請求:
- 路徑
/ - 使用
get操作
@decorator 說明
Python 中的 @something 語法被稱為「裝飾器」。
你把它放在一個函式上面。像一個漂亮的裝飾帽子(我猜這是術語的來源)。
一個「裝飾器」會對下面的函式做一些事情。
在這種情況下,這個裝飾器告訴 FastAPI 那個函式對應於 路徑 / 和 操作 get。
這就是「路徑操作裝飾器」。
你也可以使用其他的操作:
@app.post()@app.put()@app.delete()
以及更少見的:
@app.options()@app.head()@app.patch()@app.trace()
Tip
你可以自由地使用每個操作(HTTP 方法)。
FastAPI 不強制任何特定的意義。
這裡的資訊作為一個指南,而不是要求。
例如,當使用 GraphQL 時,你通常只使用 POST 操作。
第四步:定義「路徑操作函式」¶
這是我們的「路徑操作函式」:
- path:是
/。 - operation:是
get。 - function:是裝飾器下面的函式(在
@app.get("/")下面)。
from fastapi import FastAPI
app = FastAPI()
@app.get("/")
async def root():
return {"message": "Hello World"}
這就是一個 Python 函式。
它將會在 FastAPI 收到一個使用 GET 操作、網址為「/」的請求時被呼叫。
在這種情況下,它是一個 async 函式。
你也可以將它定義為一般函式,而不是 async def:
from fastapi import FastAPI
app = FastAPI()
@app.get("/")
def root():
return {"message": "Hello World"}
Note
如果你不知道差別,請查看 Async: "In a hurry?".
第五步:回傳內容¶
from fastapi import FastAPI
app = FastAPI()
@app.get("/")
async def root():
return {"message": "Hello World"}
你可以返回一個 dict、list、單個值作為 str、int 等。
你也可以返回 Pydantic 模型(稍後你會看到更多關於這方面的內容)。
有很多其他物件和模型會自動轉換為 JSON(包括 ORMs,等等)。試用你最喜歡的,很有可能它們已經有支援。
第六步:部署¶
用一行指令將你的應用程式部署到 FastAPI Cloud:fastapi deploy。🎉
關於 FastAPI Cloud¶
FastAPI Cloud 由 FastAPI 的作者與團隊打造。
它讓你以最小的成本完成 API 的建置、部署與存取流程。
它把用 FastAPI 開發應用的同樣開發者體驗帶到將應用部署到雲端的流程中。🎉
FastAPI Cloud 也是「FastAPI 與其好友」這些開源專案的主要贊助與資金提供者。✨
部署到其他雲端供應商¶
FastAPI 是開源並基於標準的。你可以把 FastAPI 應用部署到你選擇的任何雲端供應商。
依照你的雲端供應商的指南部署 FastAPI 應用吧。🤓
回顧¶
- 引入
FastAPI。 - 建立一個
app實例。 - 寫一個「路徑操作裝飾器」,像是
@app.get("/")。 - 定義一個「路徑操作函式」;例如,
def root(): ...。 - 使用命令
fastapi dev執行開發伺服器。 - 可選:使用
fastapi deploy部署你的應用程式。